
What is climate change?
This module will help students to understand:
-
What is climate?
-
What global and local influences affect climate?
-
What is meant by climate change?
Climate change means any significant change in climate, like temperature or rainfall, over a 30 year period or more. If the climate is changing, then the 30 year average temperature, or rainfall, or number of sunny days, is changing.
It is easy to mix up climate and weather.
Here’s a simple way to think about it: climate is what we expect (e.g. cold winters) and weather is what we get (e.g. rain).
Weather is what is happening in the atmosphere at any one time: how warm, windy, sunny or humid it is. Climate is the description of the average weather we might expect at a given time, usually taken for several decades or longer to average out year to year variability. Variability might be due to a particularly hot summer or very cold winter.
The world’s climate has been getting warmer since 1900. However, this overall warming has not occurred evenly across the world’s surface and different places, because of their location and geography, are affected in different ways.
The average air temperature of the Earth’s surface from 1850 – 2008
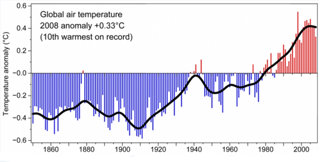
Source: Climatic Research Unit, University of East Anglia (2008) 1: Global Temperature Record. [Accessed June 2009]
-
This graphic shows the average temperature of the Earth’s surface from 1850-2008
-
The horizontal, x, axis shows time in years from 1850-2008
-
The vertical, y, axis shows how different the temperature is from the average of 1961-1990
-
Each red bar shows the world’s ‘weather’ for that year. The black line shows the changing ‘climate’
-
The climate has been getting warmer since 1900
File nameFiles
File type
Size
Download

